The Systems
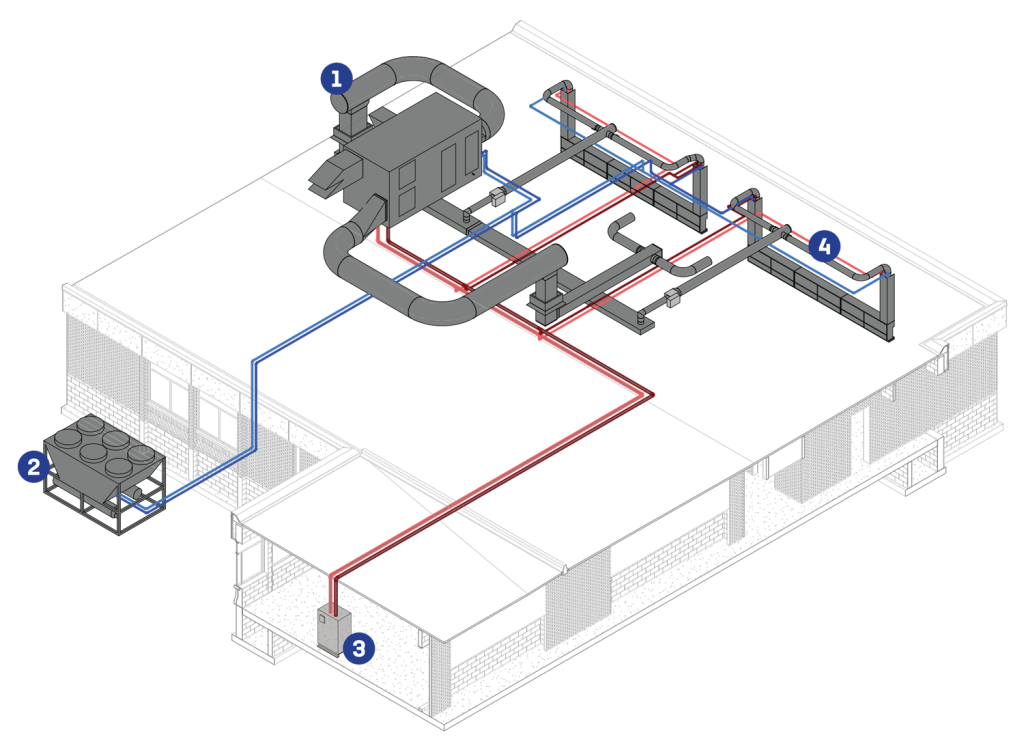
QLCI Displacement Induction
The Cornerstone of a Winning HVAC System
1. DOAS Unit
- Provides 100% dehumidified outside air for code-required ventilation needs
- Delivers verifiable outside air for occupants
- Rooftop or indoor mounting
- Shown with hot water or chilled water
- Packaged DX and gas heat suitable
- Geothermal suitable
- Typically energy recovery based
- Desiccant devices suitable
- Isolates rooms so no room-to-room airside cross-contamination occurs
2. Chiller
- Provides chilled water for QLCI and possibly DOAS chilled water coil
- Air-cooled or water-cooled suitable
- If DOAS unit is packaged DX, dedicated elevated chilled water to QLCI offers high efficiency operation
- Alternatives:
- No Chiller Design Option (only HW available) Packaged DX DOAS applied and designed to deliver cool, dehumidified primary air for recognized sensible cooling in space
- Geothermal water applied – Electrification
- Heat recovery chiller – Electrification
3. Boiler
- Provides hot water for QLCI zone heating and possibly DOAS hot water coil
- Often high efficiency condensing style boilers applied
- Gas-fired or electric boiler suitable
- Alternatives:
- If existing steam source available, apply a steam-to-hot water conversion
- Some climate designs may not require hot water in the zone
- Geothermal water applied – Electrification
- Heat recovery chiller – Electrification
4. QLCI
- Receives 100% outside air from DOAS unit to drive room air induction process across the integral coil
- Chilled water and hot water flow modulated to control sensible space loads
- Supply air delivered near the floor in displacement mode for:
- Effective removal of airborne contaminants for better IAQ
- Low velocity, temperate air for enhanced thermal comfort
- No moving parts to maintain, produce noise or consume electricity
- Provides industry-leading system efficiency due to displacement ventilation and fluid-based heat transfer
Comparative Analysis – System Technologies
DOAS-QLCI v. AHU-VAV
| DOAS-QLCI | AHU-VAV | Explanation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| IAQ – related to Ventilation Effectiveness (Ez) Cooling Mode Heating Mode | Displacement Ventilation: “purges” the occupied space 1.2 1.0-1.2 | Mixed air ventilation: dilutes but forces dirty air into occupied space 1.0 at best 0.8 | True measure of contaminant removal effectiveness; Ez > 1.0 => better IAQ (lower CO2) in room; DIV lifts contaminants up & away |
| Acoustics Why Why | <35 dBA No fan, motor, damper or compressor in room Low Velocity | >35 dBA Increased Air CFM, Higher Air Velocity, Noise potential in duct & at diffuser | DOAS delivers code minimum OA to space AHU-VAV delivers OA PLUS high % of return air for clg & htg |
| Maintenance | Vacuum coil 1x/yr | Change filters Fan bearings Motors Belts Controls | AHU uses 2/3 RA; better filtration needed. DCV necessary for limiting energy use; control points are expensive |
| System Efficiency Why Why | High Hydronic heat transfer Displacement Ventilation Reduced chiller capacity | Medium Air heat transfer Mixed air ventilation Large air handler | DOAS unit is ~1/3 CFM of AHU=>smaller ducts, coils, fans, bhp, fla, mca Reduced fan energy More efficient chiller |
| Room to Room air contamination risk | None | High % of air pulled from all rooms, mixed at air handler and returned as supply air to all rooms | DOAS-QLCI has dedicated EA pulled from room & exhausted at DOAS, no recirculation during occupied hours |
| Installed Costs | 1.0 | 0.95-1.0-1.05 | Recent feedback; DOAS-QLCI inline w/ well-designed AHU-VAV |
| Life Cycle Duration | 30+ years | 20+ years | Better practices req’d for AHU-VAV due to more moving parts |
| Installation Considerations or Risks | Low | Medium | AHU-VAV: needs considerable ceiling space for large ducts & high voltage power in rooms |
| Proprietary Technology | No | No | Hydronics piping, ducting |
| Physical Space Impact | Minimal | Minimal | |
| Occupant Comfort | High | Medium | QLCI has lower air velocities & moderate temps delivered from full-wall array. AHU-VAV can have localized drafts |
DOAS-QLCI v. DOAS-FCU
| DOAS-QLCI | DOAS-FCU | Explanation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| IAQ – related to Ventilation Effectiveness (Ez) Cooling Mode Heating Mode | Displacement Ventilation: “purges” the occupied space 1.2 1.0-1.2 | Mixed air ventilation: dilutes but forces dirty air into occupied space 1.0 at best 0.8 | True measure of contaminant removal effectiveness; Ez > 1.0 => better IAQ (lower CO2) in room; DIV lifts contaminants up & away |
| Acoustics Why Why | <35 dBA No fan, motor, damper or compressor in room Low Velocity | ≥35 dBA Single-Point HVAC device needs higher supply air velocity; Noise potential in duct & at diffuser | No moving parts in QLCI plus full-wall air delivery method allows for lower air velocity resulting quieter airflow |
| Maintenance | Vacuum coil 1x/yr | Change filters Fan bearings Motors Belts Controls | Filtration localized at DOAS unit with QLCI. Filtration needed at FCU terminal devices with FCU and VRF. Moving parts in FCU require service. |
| System Efficiency Why Why | High Hydronic heat transfer Displacement Ventilation Reduced chiller capacity | Medium Plus Air heat transfer Mixed air ventilation Larger DOAS | Higher Ez, results in smaller DOAS with DIV. No fan energy at terminal with QLCI |
| Room to Room air contamination risk | None | None | DOAS-QLCI and DOAS-FCU operate in similar manner for room-to-room contaminants |
| Installed Costs | 1.0 | 1.05-1.1 | High-voltage electrical requirements for FCU is considerable |
| Life Cycle Duration | 30+ years | 20+ years | Better maintenance practices req’d for DOAS- FCU due to more moving parts at FCU |
| Installation Considerations or Risks | Low | Medium | Similar ductwork but high voltage power req’d for FCU |
| Proprietary Technology | No | No | Hydronics piping, ducting |
| Physical Space Impact | Minimal | Minimal | |
| Occupant Comfort | High | Medium | QLCI has lower air velocities & moderate temps delivered from full- wall array. DOAS-FCU can have localized drafts |
DOAS-QLCI v. DOAS-VRF
| DOAS-QLCI | DOAS-VRF | Explanation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| IAQ – related to Ventilation Effectiveness (Ez) Cooling Mode Heating Mode | Displacement Ventilation: “purges” the occupied space 1.2 1.0-1.2 | Mixed air ventilation: dilutes but forces dirty air into occupied space 1.0 at best 0.8 | True measure of contaminant removal effectiveness; Ez > 1.0 => better IAQ (lower CO2) in room; DIV lifts contaminants up & away |
| Acoustics Why Why | <35 dBA No fan, motor, damper or compressor in room Low Velocity | ≥35 dBA Single-Point HVAC device needs higher supply air velocity; Noise potential in duct & at diffuser | No moving parts in QLCI plus full-wall air delivery method allows for lower air velocity resulting quieter airflow Maintenance Vacuum coil 1x/yr Change filters Refrigerant concerns Refrigerant growing obsolete Complexity in operating controls Filtration localized at |
| Maintenance | Vacuum coil 1x/yr | Change filters Refrigerant concerns Refrigerant growing obsolete Complexity in operating controls | Filtration localized at DOAS unit with QLCI. Filtration needed at terminal devices VRF. VRF complexity & refrigerants a service concern. |
| System Efficiency Why Why | High Hydronic heat transfer Displacement Ventilation Reduced chiller capacity | High Refrigerant heat transfer Ability to heat and cool in varied spaces | Higher Ez, results in smaller DOAS with DIV. No fan energy at terminal with QLCI. Refrigerant has high BTU capacity |
| Room to Room air contamination risk | None | None | DOAS-QLCI and DOAS-VRF operate in similar manner for room-to-room contaminants |
| Installed Costs | 1.0 | 1.0-1.05 | Recent feedback; DOAS- QLCI inline w/ DOAS-VRF, high voltage power req’d for VRF |
| Life Cycle Duration | 30+ years | 20+ years | Better practices req’d for DOAS-VRF due to more moving parts & refrigerant |
| Installation Considerations or Risks | Low | Medium | VRF: need good piping practices & high voltage power in rooms Proprietary Technology No Yes VRF has complex controls |
| Proprietary Technology | No | Yes | VRF has complex controls |
| Physical Space Impact | Minimal | Minimal | |
| Occupant Comfort | High | Medium Plus | QLCI has lower air velocities & moderate temps delivered from full- wall array. DOAS-VRF can have localized drafts |
DOAS-QLCI v. Unit Vents
| DOAS-QLCI | Unit Vents | Explanation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| IAQ – related to Ventilation Effectiveness (Ez) Cooling Mode Heating Mode | Displacement Ventilation: “purges” the occupied space 1.2 1.0-1.2 | Mixed air ventilation: dilutes but forces dirty air into occupied space 1.0 at best 0.8 | True measure of contaminant removal effectiveness; Ez > 1.0 => better IAQ (lower CO2) in room; DIV lifts contaminants up & away |
| Acoustics Why Why | <35 dBA No fan, motor, damper or compressor in room Low Velocity | ≥40 dBA, when new; Increased Air CFM Higher Air Velocity Noise potential in terminal device | DOAS delivers verifyable code minimum OA to space. UV has limited ability to prove OA % |
| Maintenance | Vacuum coil 1x/yr | Change filters Fan bearings Motors Belts Controls | Filter change outs req’d in every room; w/possible varied sizes across bldg. Poor maintenance results in shorter life span and noise |
| System Efficiency Why Why | High Hydronic heat transfer Displacement Ventilation Reduced chiller capacity | Medium to Low Air heat transfer Mixed air ventilation | Large fan power energy consumption with UV; data indicates UV can consume 30% more energy |
| Room to Room air contamination risk | None | Some, depends on bldg. practices. More concern with dust, debris and fumes from outside louver | DOAS-QLCI has dedicated EA pulled from room & exhausted at DOAS, no recirculation during occupied hours |
| Installed Costs | 1.0 | 0.75-1.0 | Depending upon type of UV; some self-contained UVs are impactful |
| Life Cycle Duration | 30+ years | 20+ years | Better practices req’d for UVs due moving parts |
| Installation Considerations or Risks | Low | Medium | Uvs require high voltage power; proper positioning of desks |
| Proprietary Technology | No | No | |
| Physical Space Impact | Minimal | Medium Plus | Similar UV protrude into room; cannot place books on top: blocks UV outlet |
| Occupant Comfort | High | Medium Plus | QLCI has lower air velocities & moderate temps delivered from full- wall array. UV can have localized drafts & noise |